Note: This is part 1 of a 3-part blog post on Nuage Networks release 5.0.
2017 began with key wins – BT, Telefonica, and Telia, among others – followed by a healthy stream of Service Provider and Enterprise wins. No less important, 2017 was also a year with a major product milestone in form of the Nuage Networks VSP 5.0 software release. Maintaining Nuage as the leading provider of SDN policy-based automation for the data center (DC) and the wide area network (WAN), the 5.0 release introduced significant product innovations and feature capabilities. As we begin the new year, it is a good time to look back at the evolution of our product palette over the last twelve months and review what we delivered in 2017.
Nuage Networks single-platform approach for the software-defined DC and SD-WAN makes it the only vendor to provide true end-to-end seamless connectivity and policy across the DC, WAN, and Public Cloud.
Our 5.0 release introduced innovations spanning all three of our product services as well as the underlying platform. To review the innovations, it is helpful to have a brief summary of our platform and the product services that derive from it:
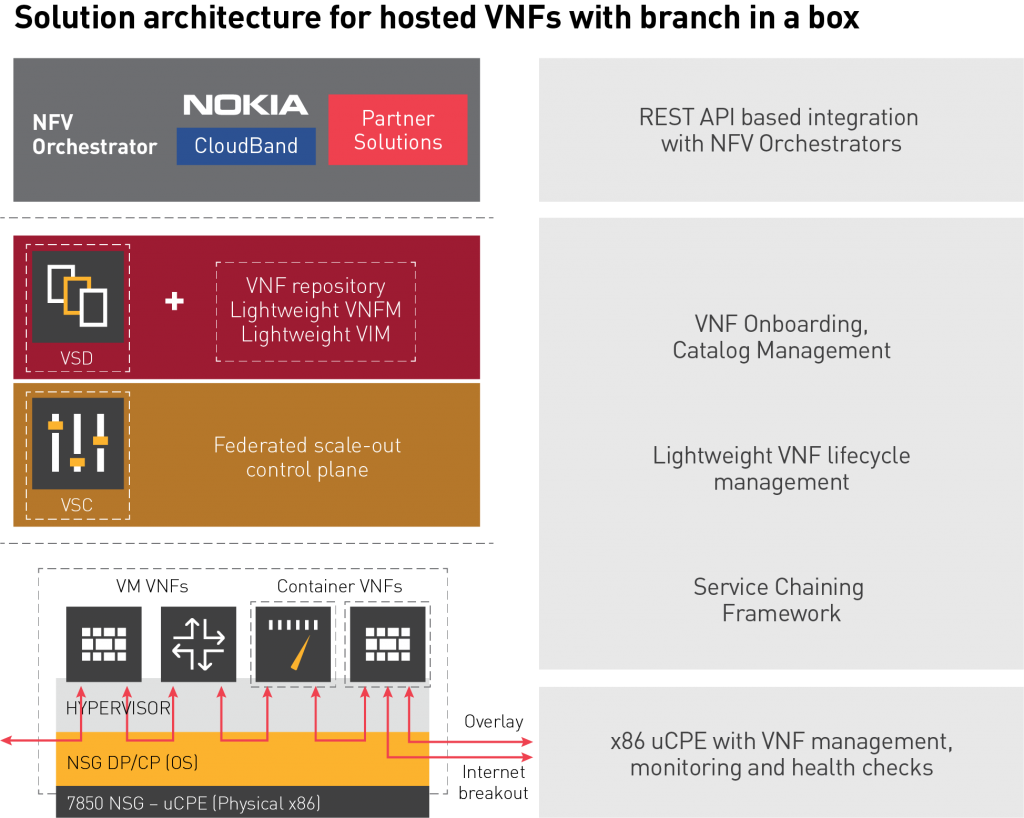
Nuage Networks Virtualized Services Platform (VSP) comprises three basic components:
- The Virtualized Services Directory (VSD), an analytics node that combines policy management with network abstractions; RESTful APIs.
- The Virtualized Services Controller (VSC), a highly scalable SDN controller that provides carrier grade routing assuring massive scale-out capabilities with MP-BGP-based federation and easy interconnection of gateways and PE routers in both DC & WAN.
- In addition to these, the data plane consists of the 7850 Network Service Gateway (NSG) or Virtualized Router & Switch (VRS)
These components deliver three services:
- Virtualized Network Services (VNS), which is essentially SD-WAN 2.0
- Virtualized Cloud Services (VCS), which addresses the software-defined data center use-case
- Virtualized Security Services (VSS), which provides software-defined security
Our 2017 innovations fall into three broad categories, called ‘themes’ in the following diagram:

This first part of the blog post addresses SD-WAN, which covers SD-WAN Beyond Connectivity and Advanced Networking with SD-WAN.
The second part of this blog post addresses SD-WAN and DC, which covers Security and Analytics for the DC and WAN.
The third and last part of this blog post will address the DC , which covers Policy-automated 100G Switching and NFV & Telco Cloud.
It is worth noting that the 5.0 release provides a significant number of new capabilities beyond those discussed in this blog, in areas such as DevOps/container networking and cloud integrations with OpenStack, VMware, and Microsoft Hyper-V/SCVMM.
SD-WAN
SD-WAN extends the concept of SDN to enterprise branch connectivity, offering a way of replacing or augmenting traditional enterprise VPN service (such as MPLS or VPLS) with a secure automated connectivity model that can work on any access network (MPLS, Internet, 3G/LTE, etc.). However, WAN connectivity is only one part of the enterprise networking puzzle. Overall, extending the value proposition of SD-WAN beyond connectivity is a key component of the Nuage Networks SD-WAN strategy as we begin 2018. It translates into immediate CapEx and operational gains that improve the SD-WAN business case for enterprises and service providers alike.
SD-WAN Beyond Connectivity
Modern enterprise sites require a range of networking value-added services (VAS) in addition to WAN connectivity. These include functions such as:
- Firewall
- URL filtering
- IPS/IDS
- NAT
- WAN Opt
- DPI/Analytics
- VOIP gateways
- Wireless LAN controllers, etc.
These functions are typically delivered as standalone appliances (physical or virtual). As such, they do not have unified cloud-based management or control, and they do require rigid/manual traffic steering to the function itself and standalone appliances do not have any direct tie-in with DC services.
Our SD-WAN solution can be used as a platform for delivering a variety of enterprise VASs. Consolidating centralized and unified policy/control for all services, seamless extension into the DC, unified interfaces to orchestration, ease of traffic selection, and chaining to and from the service functions, all add up to significant technological advantages.
For telcos, the business benefit of SD-WAN is the ability to offer on-demand, programmable VAS in addition to L2/L3 VPN connectivity.
For enterprises, the business benefit is a DevOps-style agility of service deployment, resource allocation and cost.
Nuage Networks offers two models for delivering VAS services with SD-WAN:
- Embedded on-board – services included with SD-WAN CPE software
- Service-chained functions – services hosted in a DC and chained/connected to the branch via seamless flow steering
Branch-in-a-Box
VSP 5.0 introduces a disruptive model of delivering VAS with SD-WAN. “Hosted on-premises” services (often referred to as “branch-in-a-box” or “SD-Branch”) involve hosting VAS as a virtual appliance (VM or container) on the CPE such that all the functionality needed to operate a branch is hosted in a single box with unified/secure policy and control and with lifecycle management (LCM) of that appliance.
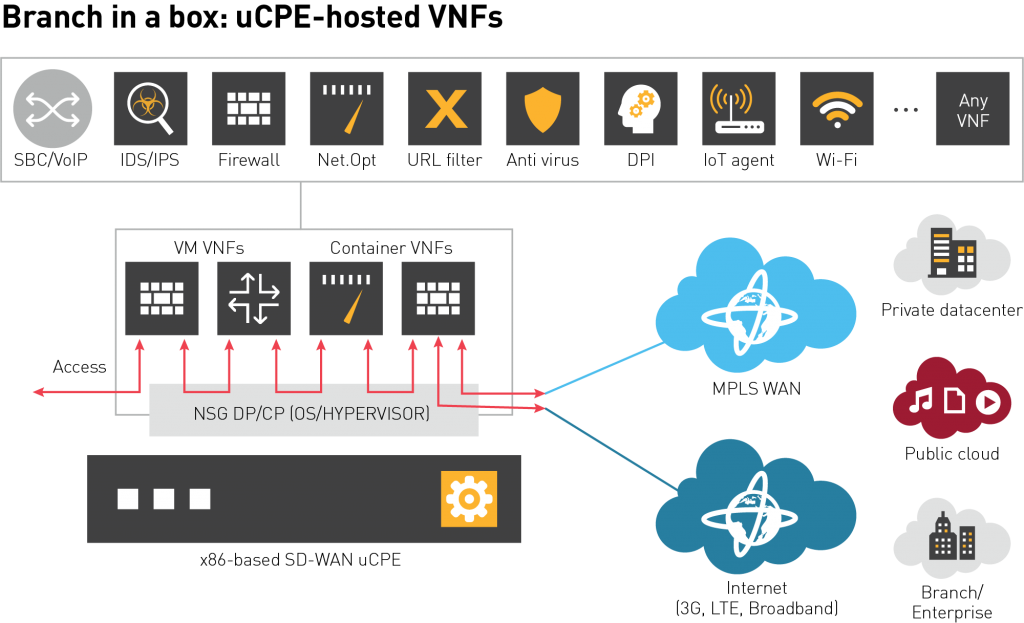
This flexible approach sets the Nuage solution apart from similar offers currently on the market through:
- Openness: Ability to host 3rd party value-added appliances via an open ecosystem that is not locked into a specific vendor’s functions.
- Self-contained VNF management: Lightweight LCM of appliances is part of the Nuage Networks offer; it does not require additional management/orchestration systems. If desired, complex LCM schemes can co-exist and be implemented outside of the SD-WAN system.
- Secure and tamper-proof operation: Our SD-WAN includes a secure, authenticated message channel between cloud policy plane and branch device. The channel is used for device bootstrapping, pushing policy/forwarding updates, and extracting SD-WAN analytics data. Nuage Networks’ “branch-in-a-box” utilizes the same channel for both VAS appliance bootstrapping and LCM, thereby ensuring fully secure, tamper-proof and encrypted operation.
- Traffic monitoring and insight: In order to derive full benefit from SDN-based automation for VAS, the system must provide pan-network flow/traffic analytics that are easy to consume via APIs and built-in visualization. The flow data can be used to automate the creation of policies based on real-time traffic, thereby dictating service chaining, mirroring and shaping for VAS traffic.
WiFi
In addition to hosting VNFs, 5.0 introduces the ability to support built-in WiFi access point (AP) capability on the CPE itself, thereby addressing the WiFi needs of small branch sites where a single AP may be sufficient. This WiFi functionality is managed by the Nuage Networks SD-WAN cloud-based policy/management plane, and includes WiFi status, user-level statistics, and public and private SSIDs with whitelists of user devices. This consolidation ensures consistent end-to-end cloud-based visibility, management, and policy plane.
Advanced Networking with SD-WAN
SD-WAN responds to two competing requirements:
- The first is cloud agility, which implies attaining the speed and efficiency of cloud-to-enterprise WAN. This is achieved by implementing application-aware routing, automated cloud policy, secure automated bootstrapping, and VAS.
- The second requirement is that the cloud coexist and interconnect with existing networks including IP VPN or VPLS sites, PE gateways, NAT devices, LAN switches, and DC virtual private cloud, etc.
Many over-the-top SD-WAN solutions on the market focus on the former requirement. The downside of this approach becomes evident as soon as the SD-WAN solution moves from PoC/demos to real world deployments where SD-WAN is no longer a standalone silo.
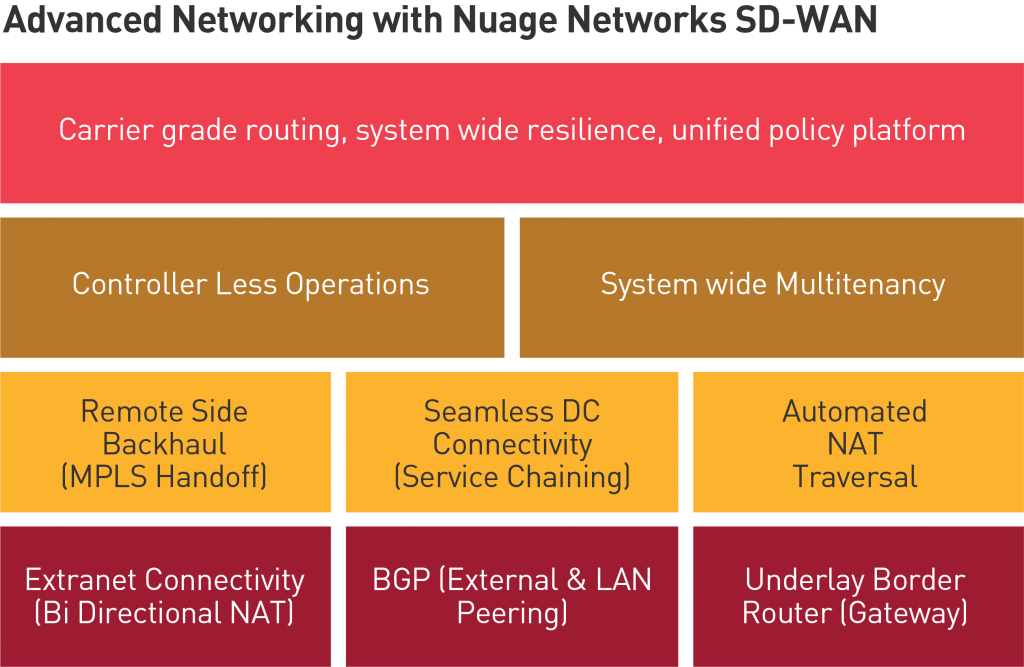
At Nuage, we have not only enabled cloud agility for SD-WAN, but also leveraged our routing heritage as part of Alcatel-Lucent/Nokia by continuing to invest in advanced networking functions for SD-WAN. In 2017, we introduced several additional advanced networking capabilities including (but not limited to):
- Underlay Border Router – UBR is a software gateway function that enables multiple SD-WAN sites residing in disjoint underlays (MPLS, internet or a combination) to communicate seamlessly with each other using automated virtual connections. UBR is available in physical form as an x86 SD-WAN CPE or as a VM to run on generic server infrastructure. Multiple UBR instances can form a cluster group offering out-of-the-box scale, load balancing and redundancy.
- Bidirectional NAT for extranet connectivity – Extranet is defined as a partial exposure of intranet to an external (but private) network. Extranets connect various partner enterprises to each other; for example, a component vendor to a manufacturer, or a credit card provider to a financial institution. Enterprise extranets are typically very tightly designed, deployed, and controlled – but cumbersome and complex to manage. Building on the SD-WAN feature set, bidirectional NAT enables enterprise extranet connectivity with the full flexibility of address range overlap by simultaneously performing source NAT (SNAT) and destination NAT (DNAT).
- Optimized Selective Breakout (Direct MPLS Handoff) – Nuage Networks SD-WAN has a variety of options to connect the SD-WAN network to a legacy MPLS network.
- One is to use a VLAN Handoff from an SD-WAN gateway to a PE device;
- Another is to do PE interworking directly, whereby the encrypted tunnels terminate at the PE and the PE is part of the extended virtual cross-connect.
- A third option introduced in 5.0 allows for selective breakout of traffic from branch CPE to a PE without requiring traversal to a central gateway function. In this scenario, the branch CPE peers directly with the PE and imports relevant IP VPN routes. This optimized breakout reduces latency and improves scale for the SD-WAN to IP VPN interface.
- LTE Uplink support – We have expanded our uplink transport options by including support for LTE/3G connections from the CPE. The LTE connectivity can serve as a primary uplink (highly desirable in certain geographic or remote locations) or a backup link of last resort.
Other advanced capabilities include:
- New CPE form factors based on the Intel x86 architecture
- Dynamic hole punching for NAT traversal
- BGP enhancements
- OSPF for LAN peering
- QoS support for voice traffic, etc.
Continue to part 2 of this blog

